Our laboratory develops space observation instruments dedicated to research in Astrophysics.
The LAM SPATIAL platform is dedicated to the Assembly, Integration and Testing of these instruments before they were launched. The description of these means remains very macroscopic but allows to have an overview of the technical capabilities of the platform. The SPATIAL platform provides the means necessary to achieve the AIT activities upon such instruments.
-
Cleanrooms
The SPATIAL platform is equipped with 1000 m² of clean rooms with all the easements and means of handling necessary for their operation. They are mainly composed by:
- ISO 8 hall: 400 m²
- ISO 8 Vibrations room: 25 m²
- ISO 7 preparation rooms: 25 m² and 30 m²
- ISO 5 optics integration rooms: 35 m², 35 m² and 40 m²
-
Vibrations testing system
Qualify the space instruments for launch
Shock and testing with sinusoidal and random excitations
 Main technical featuresThe LAM shaker serves to simulate the vibrations undergone by a satellite instrument during its launch phase in space. It is located in an ISO 8 cleanliness room which can be increased to iso 5.
Main technical featuresThe LAM shaker serves to simulate the vibrations undergone by a satellite instrument during its launch phase in space. It is located in an ISO 8 cleanliness room which can be increased to iso 5.3 vibrations axes
33 KN capability
Cleanliness level environment : ISO8 to ISO5
Air-cooled electrodynamic shaker : LDS V875/440 35 KN
Slip Low Pressure Table: LPT 600, 600mm x 600 mm
Cleanliness environment up to ISO 5 level
Spectral Dynamics SD 2560 with 28 channels
Power amplifier : LDS SPAK 35/40
Acquisition & control system : Spectral Dynamics SD 2560 with 28 channels
Piezo and ICP Accelerometers : ~ 30 ENDEVCO and ~15 B&K typesSignal conditioning
B&K 2525 pre-amp stage : 2 dedicated channels for pilot and control
B&K NEXUS : 16 voies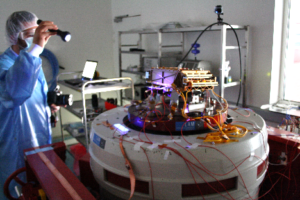 PC under Linux ‘jaguar System’
PC under Linux ‘jaguar System’
Printing curvesMain (sub)systems vibrated : NAC (Rosetta), Spire Mechanism (Herschel), NI-DS (Euclid Nisp)
The Euclid Nisp NI-DS and NI-GS vibrations campaing
Euclid is an ESA mission which will be launched in 2024 to understand the nature of the dark matter and energy. The NISP is one of the two Euclid instruments used to map the geometry of the dark Universe. The NI-DS and NI-GS are NISP detection and optical subsystems. All the NI-DS and NI-GS models (including flight one) are vibrated on the LAM vibrations testing system. The picture hereafter shows the vibrations for NI-DS Qualification model and NI-GS flight model.


-
The NAC and COL chambers
Simulate the flight space conditions
Global description


The NAC chamber
The useful volume is 2.5 m3 and its dimensions are :
- Length = 1000mm
- Width = 800 mm
- Height = 405 mm
Main technical features :
Building cleanliness level : ISO8
Vacuum level : <=10-5 mbar
Environment Temperatures range: from 353 K to 80 K
This mean can be adapted to specific test request on demand

Main (sub)systems tested : NAC (Rosetta) ; HRS (Herschel), HFI (Planck), NI-DS (Euclid Nisp) .The COL chamber
The useful volume is 0.6 m3 and its dimensions are :- Diameter = 400 mm
- Height = 400 mm

This volume consists of an opto-thermal table, a ferrule and its lid. This aluminum assembly is supported by three feet in invar connected to a damped optical bench.The COL has sixteen portholes allowing internal and external optical alignments.
Main technical features :
Building cleanliness level : ISO8
Vacuum level : <=10-5 mbar
Environment Temperatures range: from 330 K to 30 K
-
The PBEM and BE chambers
Bake out flight space components or subsystems

Global descriptionThe PBEM and the BE chambers are intended for the cleaning of satellites components or susbsystems to prevent pollution of the instrument flight optics. The useful respective volumes are 0.1 and 2 m3.
The PBEM chamber
The oven useful volume is 0.1 m3 and its dimensions are :
- Diameter = 0.45 mm
- Height = 0.65 mm
Main technical features :
Building cleanliness level : ISO8Vacuum level : <=10-5 mbar
Environment Temperatures range: from 393 K to ambient temperature
The parts to be baked out are placed in the oven and can be heated up to 120 ° C under secondary vacuum conditions and for a period of several days continuously.
Main (sub)systems baked out : NI-TC and mounts of NI-GS (Euclid Nisp) .
The BE chamber

The oven useful volume is 2 m3 and its dimensions are :- Length = 2000 mm
- Width = 1000 mm
- Height = 1000 mm
The parts to be baked out are placed in the oven and can be heated up to 120 ° C under secondary vacuum conditions and for a period of several days continuously.
Main technical features :

Building cleanliness level : ISO8Vacuum level : <=10-5 mbar
Oven Temperatures range: from 393 K to ambient temperature
Cold trap temperature : <=120 k
Main (sub)systems baked out : NI-TC and NI-GS (Euclid Nisp) .
-
The ERIOS chamber
Test satellites instruments in flight conditions
 Global description
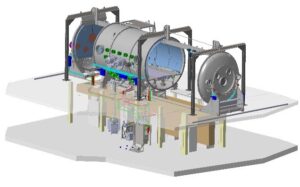
Global descriptionERIOS, the main element of the LAM platform “SPATIAL”, is a large thermal-vacuum space simulation chamber for calibration, adjustment and integration for space instruments which combines vacuum, temperature close to 80 K and an optical bench with very high mechanical stability.
The main technical features
 The useful volume is 50 m3 and the whole chamber overall dimensions are :
The useful volume is 50 m3 and the whole chamber overall dimensions are :- Diameter = 4000 mm
- Lenght = 6000 mm
Main technical features :
Building cleanliness level : ISO8
Vacuum level : <=10-5 mbar
Environment Temperatures range: from 353 K to 80 K
Optical bench size : 1.5 m * 6 m
Optical bench mechanical stability : <= 10-7 g
To ensure stability, and hence accurate measurements, the optical bench is connected to a 100-tone concrete block under the floor resting on pillars via spring boxes.
Main (sub)systems tested : Nisp STM, Nisp EM and Nisp FM (Euclid Nisp) + associated GSEs
Euclid Nisp : the first ERIOS TB/TV campaign
Euclid is an ESA mission which will be launched in 2021 to understand the nature of the dark matter and energy. The NISP is one of the two Euclid instruments used to map the geometry of the dark Universe. All the NISP models (including flight one) are fully integrated at LAM and tested in ERIOS in its flight operating environment. The picture hereafter shows the blank test configuration which is operated to perform the NISP final acceptance tests before delivery to the payload.






